官网:https://webauthn.io/
什么是webauthn?
webauthn即Web Authentication,是一个符合W3C标准的Web认证规范。它通过公私钥加密技术,实现无密码认证,用户仅需通过pin码、指纹、面部识别、usb key等方式,即可实现整套注册登录流程。使用webauthn,web网站的整个认证流程将得到极大简化,同时,相比传统的密码认证,webauthn的安全性更高。
目前主流web认证方式和wenauthn对比
目前使用最多的认证方式有三种,分别是账号密码登录、短信(邮箱)验证登录、第三方登录
账号密码登录
最古老的认证方式,缺点一大堆,大部分的密码都是弱密码,或者是与本人姓名、生日等有关的密码;大部分人的常用密码就那么几个,不管登录什么应用,都是同一个密码;偶尔换个密码,很快就忘了,账号也会忘掉。
短信(邮箱)验证登录
相比账号密码安全一些。
有时候等不到验证码,或者很慢。
用户的手机号被泄露,收到大量垃圾短信,接到大量广告电话,不胜其烦。
现在配合运营商,可以不需要验证码,实现手机号一键登录了,但是前提是,必须是正在使用流量的手机号才行,比如卡1开了5g数据连接,卡2关闭了数据连接,则手机号一键登录只支持卡1,不支持卡2.
第三方登录
用qq,微信登录完,还会强行要求你绑定手机号,没意思。
webauthn登录
不需要密码,但需要用户自己输入一个账号,可以是手机号,邮箱等。
通过设备自带的认证方式登录,比如PIN、指纹、面部识别、usb key
极简登录流程,用户体验好
安全性高,服务器不存储任何密码
缺点也有:
只能是web应用才可以
换设备登录问题
webauthn原理介绍
在介绍原理之前,先简单介绍一下公钥、私钥是什么东西,防止有人不清楚。明确以下三点,就能读懂接下来的内容:
1、公钥和私钥是成对生成的
2、公钥可以随便公开,私钥不可以泄露
3、用公钥加密的数据,只有用私钥才能解密;反之,用私钥加密的数据,也只有用公钥才能解密
公钥私钥属于非对称加密技术
webauthn流程介绍
首先明确,在webauthn认证流程中,有三个参与者:
1、后端服务server
2、浏览器
3、用户设备中的认证器:比如Windows Hello,MacOS的Touch ID,他负责生成公私钥,签名。
注册流程

1、用户输入username(理解为账号,可以是手机号、邮箱等),前端发起注册请求,把username传到后端
2、后端拿到username后,先验证该username是否被注册;然后生成挑战;然后将username、挑战缓存起来(可以用session或redis);然后返回给前端挑战、用户信息、依赖方信息
(1)挑战:一个随机的ByteArray转成的base64字符串
(2)用户信息:包含id,name,displayName;id由后端随机生成(出于安全考量,这应尽可能不与任何用户信息相关联,如不要包含用户名、用户邮箱等),name即username,displayName为展示名,可以随便。(3)依赖方信息:包含后端指定的签名算法、认证方式、所在域名等信息
3、浏览器请求认证器,生成公钥私钥,请求认证器的具体方式如下:
navigator.credentials.create(credentialCreateOptions).then(publicKeyCredential => {
console.log(publicKeyCredential)
}) 其中,参数credentialCreateOptions比较复杂,他包含这些内容:
{
publicKey: {
challenge, //挑战
rp: { //依赖方信息
id,
name
},
user: { //用户信息
id,
name,
displayName
},
pubKeyCredParams: [ //算法列表
{
type: "public-key",
alg
}
],
authenticatorSelection: { //指定的认证器类型(可选)
authenticatorAttachment,
userVerification
},
excludeCredentials: [ //用于标识要排除的凭证
{
id,
transports: [],
type: "public-key"
}
],
timeout //超时时间
}
} 参数说明如下:
challenge: Uint8Array:转换为Uint8Array的挑战,长度至少为 16,建议为 32rp: Object:依赖方信息,其中有一项为必须:rp.id: String:(可选)依赖方 ID,必须为当前域名或为当前域名的子集的域名(不是子域名)。如域名为test.123.example.com,则依赖方 ID 可以是test.123.example.com,123.example.com或example.com。不指定则默认使用当前域名rp.name: String:依赖方名称,用于方便用户辨认
user: Object:用户信息,其中有三项为必须:user.id: Uint8Array:转换为Uint8Array的字符串。出于安全考量,这应尽可能不与任何用户信息相关联,如不要包含用户名、用户邮箱等user.name: String:登录用户名user.dispalyName: String:用于显示的用户名称,显示与否的具体行为取决于浏览器
pubKeyCredParams: Array:一个算法列表,指明依赖方接受哪些签名算法。列表的每一项都是一个对象,拥有两个属性:pubKeyCredParams[].type: String:值只能为 "public-key"pubKeyCredParams[].alg: Number:一个负整数,用于标明算法。具体算法对应的数字可以在 COSE 找到
authenticatorSelection: Object:(可选)用于过滤正确的认证器,这里介绍常用的一个参数:authenticatorSelection.authenticatorAttachment: String:(可选)指定要求的认证器类型。如果没有满足要求的认证器,认证可能会失败。该参数可以为null(表示接受所有类型的认证器)或是以下两个值之一:platform:表示仅接受平台内置的、无法移除的认证器,如手机的指纹识别设备cross-platform:表示仅接受外部认证器,如 USB Key
authenticatorSelection.userVerification: String:(可选)指定认证器是否需要验证“用户为本人 (User Verified, UV)”,否则只须“用户在场 (User Present, UP)”。具体验证过程取决于认证器(不同认证器的认证方法不同,也有认证器不支持用户验证),而对验证结果的处理情况则取决于依赖方。该参数可以为以下三个值之一:required:依赖方要求用户验证preferred:(默认)依赖方希望有用户验证,但也接受用户在场的结果discouraged:依赖方不关心用户验证。对于 iOS/iPad OS 13,必须设置为此值,否则验证将失败
excludeCredentials: Array:(可选)用于标识要排除的凭证,可以避免同一个用户多次注册同一个认证器。如果用户试图注册相同的认证器,用户代理会抛出InvalidStateError错误。数组中的每一项都是一个公钥凭证对象,包含以下属性:excludeCredentials[].type: String:值只能为 "public-key"excludeCredentials[].id: Uint8Array:要排除的凭证 IDexcludeCredentials[].transports: Array:(可选)用于指定该凭证所需的认证器与用户代理的通信方式,可以包含以下的一或多个字符串:usb:可以通过 USB 连接的认证器nfc:可以通过 NFC 连接的认证器ble:可以通过蓝牙连接的认证器internal:平台内置的、无法移除的认证器
timeout: Number:(可选)方法超时时间的毫秒数,超时后将强制终止create()并抛出错误。若不设置,将使用用户代理的默认值;若太大或太小,则使用最接近的用户代理默认值范围中的值。推荐值为 5000-120000
返回值PublicKeyCredential 包含以下字段:
{
rawId: ArrayBuffer(32) {},
response: AuthenticatorAttestationResponse {
attestationObject: ArrayBuffer(390) {},
clientDataJSON: ArrayBuffer(121) {}
},
id: "VByF2w2hDXkVsevQFZdbOJdyCTGOrI1-sVEzOzsNnY0",
type: "public-key"
} id: String:Base64URL 编码的凭证 IDrawId: ArrayBuffer:ArrayBuffer的原始凭证 IDtype: String:一定是 "public-key"response: Object:AuthenticatorAttestationResponse对象,是PublicKeyCredential的主要部分,包含以下两个内容:response.clientDataJSON: ArrayBuffer:客户端数据,包含 origin(即凭证请求来源)、挑战等信息response.attestationObject: ArrayBuffer:CBOR 编码的认证器数据,包含凭证公钥、凭证 ID、签名(如果有)、签名计数等信息
4、用户授权生成密钥对,通过PIN、指纹、面部识别等方式
5、前端讲上一步认证器返回的结果传到后端,进行注册验证
6、后端首先校验前端传过来的挑战是否和自己缓存中的一致;然后利用公钥解密签名,解密后的签名应该和挑战一致;最后保存公钥和认证信息,整个注册流程完成。
登录流程
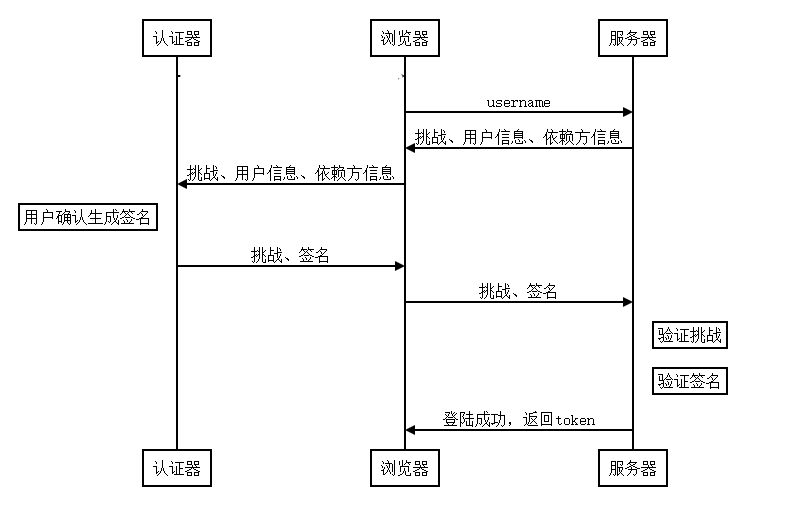
1、浏览器向服务器发送登陆请求,携带username
2、服务器向浏览器发送挑战,并缓存挑战
3、浏览器向认证器发送挑战、依赖方信息和客户端信息,请求对挑战签名
4、认证器请求用户授权动作,随后通过依赖方信息找到对应私钥,并使用私钥签名挑战(即断言),交给浏览器
5、浏览器将签名后的挑战发送给服务器
6、服务器用之前存储的公钥验证挑战是否与发送的一致,一致则验证成功,返回token
其中第三步,浏览器向认证器请求签名的实现方式如下:
navigator.credentials.get(credentialGetOptions).then(publicKeyCredential =>{
console.log(publicKeyCredential);
}) 参数credentialGetOptions包含以下字段:
{
publicKey: {
challenge,
rpId,
userVerification,
allowCredentials: [
{
id,
transports: [],
type: "public-key"
}
],
timeout
}
} challenge: Uint8Array:转换为Uint8Array的挑战,长度至少为 16,建议为 32rpID: String:(可选)依赖方 ID,需要和注册认证器时的一致。规则和上述的rp.id一致,不指定默认使用当前域名userVerification: String:和上文一样,只是需要注意它这次不在authenticatorSelection中了allowCredentials: Array:(可选)用于标识允许的凭证 ID,使用户代理找到正确的认证器。只有符合这个列表中凭证 ID 的凭证才能被成功返回。数组中的每一项都是对象,包含以下属性:allowCredentials[].type: String:值只能为 "public-key"allowCredentials[].id: Uint8Array:允许的凭证 IDallowCredentials[].transports: Array:(可选)用于指定该凭证所需的认证器与用户代理的通信方式,可以包含以下的一或多个字符串:usb:可以通过 USB 连接的认证器nfc:可以通过 NFC 连接的认证器ble:可以通过蓝牙连接的认证器internal:平台内置的、无法移除的认证器
timeout: Number:(可选)方法超时时间的毫秒数,和上面的一样,推荐值为 5000-120000
返回值publicKeyCredential包含以下字段:
{
rawId: ArrayBuffer(32) {},
response: AuthenticatorAssertionResponse {
authenticatorData: ArrayBuffer(37) {},
signature: ArrayBuffer(256) {},
userHandle: ArrayBuffer(64) {},
clientDataJSON: ArrayBuffer(118) {}
}
id: "VByF2w2hDXkVsevQFZdbOJdyCTGOrI1-sVEzOzsNnY0"
type: "public-key"
} id: String:Base64URL 编码的凭证 IDrawId: ArrayBuffer:ArrayBuffer的原始凭证 IDtype: String:一定是 "public-key"response: Object:对于验证流程,认证会返回AuthenticatorAssertionResponse而不是AuthenticatorAttestationResponse对象,这个对象包含以下 4 个属性:response.authenticatorData: ArrayBuffer:认证器信息,包含认证状态、签名计数等response.signature: ArrayBuffer:被认证器签名的authenticatorData+clientDataHash(clientDataJSON的 SHA-256 hash)response.userHandle: ArrayBuffer:create()创建凭证时的用户 IDuser.id。许多 U2F 设备不支持这一特性,这一项将会是nullresponse.clientDataJSON: ArrayBuffer:客户端数据,包含 origin(即凭证请求来源)、挑战等信息
演示视频
windows端:
安卓手机chrome浏览器(黑屏是因为输入指纹的时候,系统不允许录制,被禁了):
苹果手机:
mac演示:
苹果扫码登录mac端(这个功能我没能在安卓上测试成功):
关于webauthn的几个缺点
1、多设备登录问题
由于私钥存储在设备中,换设备登录会比较麻烦,有两种办法:
(1)支持多设备绑定,即一个用户可以对应多个公钥,这需要通过业务开发才能支持
(2)设备与设备之间打通,就是说,当前账号是在我手机上注册的,如果我想在电脑上登录,那么电脑和手机互联,电脑把相关数据变成二维码,手机扫码完成签名发送到电脑,从而完成认证。上面视频中扫码演示的,便是这个功能,但是只在mac与ios中测试成功了,在windows与安卓的组合中并未成功,具体原因不清楚。
2、文档不全,生态不够好
国内关于webauthn的中文文档十分少;webauthn方法的相关框架也不多,使用webauthn技术的网站也不多(压根没见到),生态不够好。
3、不能作为唯一的认证方式
webauthn仅限于浏览器中使用,且考虑到设备更换、设备丢失等,可能还是需要额外绑定手机、邮箱等作为账号找回的手段。也可以把webauthn作为二次认证的方式。
4、必须在https的环境中使用
如果你在调试的时候,浏览器控制台报这个错误:
Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'create')
at http://192.168.1 .209 :9093/webauthntest :59
at ......
.... 那很有可能是因为你的测试环境不是在127.0.0.1或者https域名下,假如不是在这两种环境下,浏览器会认为当前环境不安全,navigator.credentials将返回undefined
哪些浏览器支持webauthn?
Google Chrome 67 或更高版本
Microsoft Edge 85 或更高版本
Safari 14 或更高版本
参考文章
https://flyhigher.top/develop/2160.html
附录:整套流程代码实现
前端:jquery
后端:springboot
前端先画个username输入框,一个登录按钮,一个注册按钮代码:
<div style="margin: 0 auto;width: 300px;text-align: center" >
<h4 style="display: block">Webauthn Test</h4>
<input type="text" id="username" placeholder="userName" class="form-control"/>
<div style="display: flex;justify-content: space-between;margin-top: 10px;">
<button class="btn-primary" id="btn-log" style="flex: 1">Login</button>
<button class="btn-danger" id="btn-reg" style="flex: 1">Register</button>
</div>
</div>
<script type="module">
//webauthn.js是对后端api接口的封装,不具体展示了
import {register, registerauth, login, finishLogin} from '../static/js/webauthn.js'
//为注册按钮绑定时间
$('#btn-reg').click(function () {
let val = $('#username').val();
if (!val) {
return;
}
register({userName: val, displayName: val}, res => {
if (res.success) {
let credentialCreateJson = JSON.parse(res.result)
let credentialCreateOptions = {
publicKey: {
...credentialCreateJson.publicKey,
challenge: base64urlToUint8array(credentialCreateJson.publicKey.challenge),
user: {
...credentialCreateJson.publicKey.user,
id: base64urlToUint8array(credentialCreateJson.publicKey.user.id),
},
excludeCredentials: credentialCreateJson.publicKey.excludeCredentials.map(credential => ({
...credential,
id: base64urlToUint8array(credential.id),
})),
extensions: credentialCreateJson.publicKey.extensions,
}
}
console.log('credentialCreateOptions:')
console.log(credentialCreateOptions)
navigator.credentials.create(credentialCreateOptions).then(publicKeyCredential => {
console.log('publicKeyCredential')
console.log(publicKeyCredential)
return {
type: publicKeyCredential.type,
id: publicKeyCredential.id,
response: {
attestationObject: uint8arrayToBase64url(publicKeyCredential.response.attestationObject),
clientDataJSON: uint8arrayToBase64url(publicKeyCredential.response.clientDataJSON),
transports: publicKeyCredential.response.getTransports && publicKeyCredential.response.getTransports() || [],
},
clientExtensionResults: publicKeyCredential.getClientExtensionResults(),
}
}).then(encodedResult => {
// const form = document.getElementById("form");
// const formData = new FormData(form);
console.log('encodedResult')
console.log(encodedResult)
// formData.append("credential", JSON.stringify(encodedResult));
let param = {username: val, credential: JSON.stringify(encodedResult)};
registerauth(param, function (res) {
console.log(res)
if (res.success) {
alert('注册成功')
} else {
alert(res.errorDesc)
}
})
})
}
})
});
//为登录按钮绑定事件
$('#btn-log').click(function () {
let val = $('#username').val();
if (!val) {
return;
}
login({username: val}, function (res) {
if (!res.success) {
alert(res.errorDesc)
}
let credentialGetJson = JSON.parse(res.result);
let credentialGetOptions = {
publicKey: {
...credentialGetJson.publicKey,
allowCredentials: credentialGetJson.publicKey.allowCredentials
&& credentialGetJson.publicKey.allowCredentials.map(credential => ({
...credential,
id: base64urlToUint8array(credential.id),
})),
challenge: base64urlToUint8array(credentialGetJson.publicKey.challenge),
extensions: credentialGetJson.publicKey.extensions,
},
};
console.log(credentialGetOptions);
navigator.credentials.get(credentialGetOptions).then(publicKeyCredential =>{
let encodedResult = {
type: publicKeyCredential.type,
id: publicKeyCredential.id,
response: {
authenticatorData: uint8arrayToBase64url(publicKeyCredential.response.authenticatorData),
clientDataJSON: uint8arrayToBase64url(publicKeyCredential.response.clientDataJSON),
signature: uint8arrayToBase64url(publicKeyCredential.response.signature),
userHandle: publicKeyCredential.response.userHandle && uint8arrayToBase64url(publicKeyCredential.response.userHandle),
},
clientExtensionResults: publicKeyCredential.getClientExtensionResults(),
}
console.log(encodedResult);
return encodedResult;
}).then(encodedResult => {
let params = {
username: val,
credential: JSON.stringify(encodedResult)
}
finishLogin(params, function (res) {
if (res.success) {
alert('登陆成功')
} else {
alert(res.errorDesc)
}
})
})
})
})
</script>
<script>
function base64urlToUint8array(base64Bytes) {
const padding = '===='.substring(0, (4 - (base64Bytes.length % 4)) % 4);
return base64js.toByteArray((base64Bytes + padding).replace(/\//g, "_").replace(/\+/g, "-"));
}
function uint8arrayToBase64url(bytes) {
if (bytes instanceof Uint8Array) {
return base64js.fromByteArray(bytes).replace(/\+/g, "-").replace(/\//g, "_").replace(/=/g, "");
} else {
return uint8arrayToBase64url(new Uint8Array(bytes));
}
}
class WebAuthServerError extends Error {
constructor(foo = 'bar', ...params) {
super(...params)
this.name = 'ServerError'
this.foo = foo
this.date = new Date()
}
}
function throwError(response) {
throw new WebAuthServerError("Error from client", response.body);
}
function checkStatus(response) {
if (response.status !== 200) {
throwError(response);
} else {
return response;
}
}
function initialCheckStatus(response) {
checkStatus(response);
return response.json();
}
function followRedirect(response) {
if (response.status == 200) {
window.location.href = response.url;
} else {
throwError(response);
}
}
function displayError(error) {
const errorElem = document.getElementById('errors');
errorElem.innerHTML = error;
console.error(error);
}
</script> 后端:
使用框架实现,先引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.yubico</groupId>
<artifactId>webauthn-server-core</artifactId>
<version>1.12.1</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency> 需要重写CredentialRepository
package com.zjh.znwz.service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import com.yubico.webauthn.CredentialRepository;
import com.yubico.webauthn.RegisteredCredential;
import com.yubico.webauthn.data.ByteArray;
import com.yubico.webauthn.data.PublicKeyCredentialDescriptor;
import com.zjh.common.entity.WebauthUser;
import com.zjh.znwz.dao.WebauthUserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import lombok.Getter;
@Repository
@Getter
public class RegistrationService implements CredentialRepository {
@Autowired
private WebauthUserMapper webauthUserMapper;
@Override
public Set<PublicKeyCredentialDescriptor> getCredentialIdsForUsername(String username) {
List<WebauthUser> webauthUsers = webauthUserMapper.selectByUsername(username);
return webauthUsers.stream()
.map(
webauthUser ->
PublicKeyCredentialDescriptor.builder()
.id(ByteArray.fromBase64(webauthUser.getCredentialId()))
.build())
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
}
@Override
public Optional<ByteArray> getUserHandleForUsername(String username) {
List<WebauthUser> webauthUsers = webauthUserMapper.selectByUsername(username);
return Optional.of(ByteArray.fromBase64(webauthUsers.get(0).getHandle()));
}
@Override
public Optional<String> getUsernameForUserHandle(ByteArray userHandle) {
List<WebauthUser> webauthUsers = webauthUserMapper.selectByHandle(userHandle.getBase64());
return Optional.of(webauthUsers.get(0).getUsername());
}
@Override
public Optional<RegisteredCredential> lookup(ByteArray credentialId, ByteArray userHandle) {
WebauthUser webauthUsers = webauthUserMapper.selectOneByCredentialIdAndHandle(credentialId.getBase64(), userHandle.getBase64());
Optional<WebauthUser> auth = Optional.of(webauthUsers);
return auth.map(
credential ->
RegisteredCredential.builder()
.credentialId(ByteArray.fromBase64(credential.getCredentialId()))
.userHandle(ByteArray.fromBase64(credential.getHandle()))
.publicKeyCose(ByteArray.fromBase64(credential.getPublicKey()))
// .signatureCount(credential.getCount())
.build()
);
}
@Override
public Set<RegisteredCredential> lookupAll(ByteArray credentialId) {
List<WebauthUser> auth = webauthUserMapper.selectByCredentialId(new String(credentialId.getBytes()));
return auth.stream()
.map(
credential ->
RegisteredCredential.builder()
.credentialId(ByteArray.fromBase64(credential.getCredentialId()))
.userHandle(ByteArray.fromBase64(credential.getHandle()))
.publicKeyCose(ByteArray.fromBase64(credential.getPublicKey()))
// .signatureCount(credential.getCount())
.build())
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
}
} 初始化RelyingParty,放入容器中
package com.zjh.znwz.config;
import com.yubico.webauthn.RelyingParty;
import com.yubico.webauthn.data.RelyingPartyIdentity;
import com.zjh.znwz.service.RegistrationService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.HashSet;
/**
* @author 1
* @date 2023-02-01 11:32
**/
@Configuration
public class RelyingPartyConfig {
//@Value("${webauthn.host}")
private String host = "http://localhost:9093";
// @Value("${webauthn.id}")
private String webauthnId = "localhost";
@Bean
public RelyingParty relyingParty(RegistrationService regisrationRepository) {
RelyingPartyIdentity rpIdentity = RelyingPartyIdentity.builder()
.id(webauthnId)
.name("webauthntest")
.build();
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(host);
return RelyingParty.builder()
.identity(rpIdentity)
.credentialRepository(regisrationRepository)
.origins(set)
.build();
}
} controller代码:
package com.zjh.znwz.controller;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.yubico.webauthn.*;
import com.yubico.webauthn.data.*;
import com.yubico.webauthn.exception.AssertionFailedException;
import com.yubico.webauthn.exception.RegistrationFailedException;
import com.zjh.common.entity.WebauthUser;
import com.zjh.common.page.Result;
import com.zjh.znwz.dao.WebauthUserMapper;
import com.zjh.znwz.utils.RedisUtil;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.server.ResponseStatusException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author 1
* @date 2023-01-31 14:56
**/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/webauthn")
public class TestWebauthnController {
private final WebauthUserMapper webauthUserMapper;
private final RelyingParty relyingParty;
private final RedisUtil redisUtil;
public TestWebauthnController(WebauthUserMapper webauthUserMapper, RelyingParty relyingParty, RedisUtil redisUtil) {
this.webauthUserMapper = webauthUserMapper;
this.relyingParty = relyingParty;
this.redisUtil = redisUtil;
}
@PostMapping("/register")
@ResponseBody
public Result register(@RequestBody Map<String, String> map, HttpSession session) throws JsonProcessingException {
String userName = map.get("userName");
String displayName = map.get("displayName");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(userName) || StringUtils.isEmpty(displayName)) {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
//验证userName是否已被注册
List<WebauthUser> webauthUsers = webauthUserMapper.selectByUsername(userName);
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(webauthUsers)) {
throw new RuntimeException("userName已被注册");
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[32];
new SecureRandom().nextBytes(bytes);
UserIdentity userIdentity = UserIdentity.builder()
.name(userName)
.displayName(displayName)
.id(new ByteArray(bytes))
.build();
System.out.println(userIdentity.getId().getBase64());
StartRegistrationOptions registrationOptions = StartRegistrationOptions.builder()
.user(userIdentity)
.build();
PublicKeyCredentialCreationOptions registration = relyingParty.startRegistration(registrationOptions);
redisUtil.set("register-" + userName, registration.toJson(), 300);
try {
String s = registration.toCredentialsCreateJson();
System.out.println(s);
return Result.success(s);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, "Error processing JSON.", e);
}
}
@PostMapping("/registerauth")
@ResponseBody
public Result registerauth(@RequestBody Map<String, String> map, HttpSession session) {
String username = map.get("username");
String credential = map.get("credential");
try {
Object o = redisUtil.get("register-" + username);
if (o == null) {
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, "Cached request expired. Try to register again!");
}
PublicKeyCredentialCreationOptions requestOptions = PublicKeyCredentialCreationOptions.fromJson(o.toString());
if (requestOptions != null) {
PublicKeyCredential<AuthenticatorAttestationResponse, ClientRegistrationExtensionOutputs> pkc =
PublicKeyCredential.parseRegistrationResponseJson(credential);
FinishRegistrationOptions options = FinishRegistrationOptions.builder()
.request(requestOptions)
.response(pkc)
.build();
RegistrationResult result = relyingParty.finishRegistration(options);
String credentialId = result.getKeyId().getId().getBase64();
String publicKey = result.getPublicKeyCose().getBase64();
WebauthUser webauthUser = new WebauthUser();
webauthUser.setCredentialId(credentialId);
webauthUser.setDisplayName(username);
webauthUser.setPublicKey(publicKey);
webauthUser.setHandle(requestOptions.getUser().getId().getBase64());
webauthUser.setUsername(username);
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(webauthUser));
webauthUserMapper.insert(webauthUser);
return Result.success();
} else {
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, "Cached request expired. Try to register again!");
}
} catch (RegistrationFailedException e) {
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.BAD_GATEWAY, "Registration failed.", e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST, "Failed to save credenital, please try again!", e);
}
}
@PostMapping("/login")
@ResponseBody
public Result login(@RequestBody Map<String, String> map, HttpSession session) {
String username = map.get("username");
List<WebauthUser> webauthUsers = webauthUserMapper.selectByUsername(username);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(webauthUsers)) {
throw new RuntimeException("用户名不存在");
}
AssertionRequest request = relyingParty.startAssertion(StartAssertionOptions.builder()
.username(username)
.build());
try {
redisUtil.set("login-" + username, request.toJson());
return Result.success(request.toCredentialsGetJson());
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST, e.getMessage());
}
}
@PostMapping("/finishLogin")
@ResponseBody
public Result finishLogin(@RequestBody Map<String, String> map, HttpSession session) {
String username = map.get("username");
String credential = map.get("credential");
try {
PublicKeyCredential<AuthenticatorAssertionResponse, ClientAssertionExtensionOutputs> pkc;
pkc = PublicKeyCredential.parseAssertionResponseJson(credential);
Object o = redisUtil.get("login-" + username);
AssertionRequest request = AssertionRequest.fromJson(o.toString());
AssertionResult result = relyingParty.finishAssertion(FinishAssertionOptions.builder()
.request(request)
.response(pkc)
.build());
if (result.isSuccess()) {
return Result.success();
} else {
return Result.fail("登陆失败");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Authentication failed", e);
} catch (AssertionFailedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Authentication failed", e);
}
}
} 







高谈阔论